The Key Work of Photovoltaic Power Plant Operation and Maintenance
The Key Work of Photovoltaic Power Plant Operation and Maintenance
1. Work before the project is handed over to operation and maintenance
The information handed over by the general contractor (or construction party) of the photovoltaic power station to the operation and maintenance team must be complete, mainly including:
1) Preliminary information: preliminary work approval documents, such as land approval, environmental impact assessment approval, access approval, etc.;
2) Technical data: design drawings, equipment technical data, project acceptance documents;
3) Contract and financial documents: bidding documents, equipment and material purchase contracts, various expenses, etc.;
For the acquired power station, when performing due diligence, firstly, verify the legality, completeness and validity of the above-mentioned documents, relevant procedures involved, contracts and other materials; secondly, it is necessary to test and evaluate the overall quality of the power station to ensure Complete the rectification work before the power station is handed over.

2. Preparations for power station operation and maintenance
The photovoltaic power station taken over by the operation and maintenance team first needs to formulate a reasonable operation and maintenance division of labor and a scientific management system according to its own power station and staffing situation, including:
1) Production and operation system, 2) Safety management system, 3) Emergency fire protection system, 4) Equipment operation rules, etc.;
1. Production and operation system
Clear regulations should be made for daily inspection work. Regular inspections and inspections under special circumstances are essential to grasp the operating status of the power station in time, discover existing or potential problems, and ensure normal power generation.
2. Safety management system
Safety management runs through the entire process of operation and maintenance, including the rational use of safety tools and safe operation specifications to ensure personal safety and equipment safety. Since novices have limited on-site operation skills and experience in fault judgment and analysis, skilled personnel are required to train them. For the high-voltage electrical part, a high-voltage operation network access permit is also required before they can work with the certificate.
3. Fault analysis in power station operation and maintenance
During the operation of photovoltaic power plants, due to factors such as the equipment itself, weather and other force majeure, failures will occur on both the DC side and the AC side.
After one year of continuous tracking of a western ground power station, it was found that the total fault frequency of the DC side (components, combiner boxes, inverters, DC cables) accounted for about 90% of the total faults, while the AC side (AC cables, Substation, civil engineering and step-up station) and other aspects of failure accounted for a relatively small proportion.
Monitoring a number of power stations that have been in normal operation for more than 2 years in a certain area in the west, the annual loss of power generation due to failure is the smallest about 0.18%, and the largest is about 0.85%. The frequency of main equipment failures in photovoltaic power stations and scale, as shown in the figure below.
(Note: Due to the large individual differences of photovoltaic power plants, the data in this case are not widely representative).
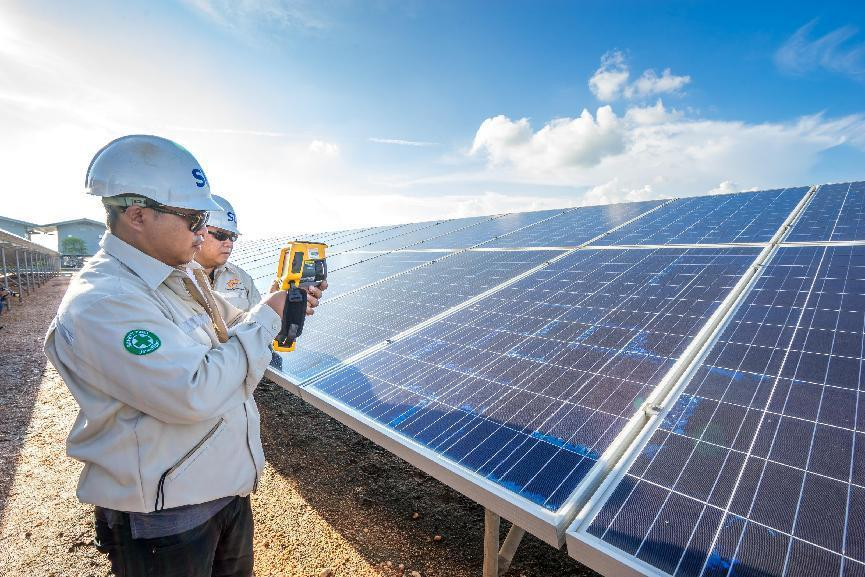

Inverters, step-up stations, and pooling cables have less frequent failures, but once they fail, they will have a great impact on power generation. The failure can be seen from the real-time running status of the background monitoring, and timely maintenance can be carried out.
Due to the large number of strings on the DC side and the high frequency of failures (accounting for 73.5%), the square array strings on the DC side have a great impact on power generation; however, their faults are not easy to be found. , can significantly increase the power generation of the power station.
1. The main failure of the component
During the operation and maintenance process, the main problems of components include: loose components, hot spot failure, glass breakage, junction box diode failure, etc.
Main reasons:
- Unfastened pressure blocks during construction lead to loosening of components;
- It is related to the quality of the component itself.
2. The main fault of the combiner box
The main faults and causes of the combiner box are shown in the table below:
- The fuse is burned out, mainly due to the quality of the fuse or the rated current of the selected fuse is too small
- The circuit breaker generates heat and trips
- Abnormal communication (including damage to the communication acquisition module of the combiner box)
- The wiring terminals heat up, mainly due to loose terminals and excessive resistance),
- Branch faults, such as ground faults, overcurrent, DC arcing, etc.
3. The main failure of the inverter
1) Generally, due to poor exhaust system and high temperature of the cabinet, the module (main board) fails
2) The heat dissipation of the module itself causes the module to overheat
3) Fan damage problem
4) The fuse is burned out
5) Smoke detector failure
6) Circuit breaker tripped
7) Abnormal startup
8) Ground fault, etc.
4. Main faults of DC cables
1) Ground fault
2) Caused by construction or damaged by vehicle rolling insulation
3) Cable head breakdown problem
4) The design of the design institute does not match the actual situation, and the wire diameter is small, which causes the cable to heat up
5) Short circuit, etc.
If the buried depth of the cable is shallow during construction, especially if the soil of some ground power stations is gravel, it is easy for the operation and maintenance vehicle to crush the cable and cause damage to it when passing by.
5. Other issues
The foundation of the power station has subsided, or the ground has collapsed due to rainwater erosion, causing the supports to tilt, and some have not taken flood control measures. Outdoor oily box substations mainly have problems such as oil leakage, low oil level, and circuit breaker failure.
6. Summary of power station faults
During the operation of the power station, the above-mentioned common faults may recur in the future, or new problems may be exposed. What we need to do is to regularly analyze and classify the faults through the above-mentioned similar methods. To deal with, strengthen inspections in areas where faults occur frequently, and minimize fault losses as much as possible. On the other hand, the process of fault discovery, analysis, and resolution is also one of the ways for operation and maintenance personnel to improve their own capabilities.
7. Power station intelligent operation and maintenance system
With the increasing scale of photovoltaic power plants owned by enterprises, the traditional power plant management methods are no longer applicable. The power plant operation and maintenance system tailored for power plant operation and maintenance came into being. It not only reduces the workload of operation and maintenance personnel , and the system is also very powerful, able to complete:
Data collection and analysis (meteorological data, power generation statistics, PR analysis, equipment operation)
String fault location, alarm center, defect management, automated report management and other functions.
Among them, data collection and analysis is the core of the operation and maintenance system. The data collected and analyzed include:
Combiner box data (string current, voltage)
Inverter data (real-time voltage, power generation, real-time power, etc.)
Real-time data of key points such as box-type substation, high-voltage side, grid-connected point, etc.
The operation and maintenance system is based on real-time data, which makes the operation and maintenance of the power station more efficient and is a very effective technical means.
However, it must be emphasized that even with the operation and maintenance system, the daily inspection work still needs to continue!
Some problems are blind spots for the operation and maintenance system, which are difficult to find. For example, there is no effective real-time monitoring method for the temperature of the equipment terminal. Infrared scanning is performed on the equipment terminals of the photovoltaic area and the booster station to find abnormal temperature points and eliminate hidden dangers in the bud.